What is functional programming
- Functional programming is a programming paradigm — a style of building the structure and elements of computer programs — that treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions and avoids changing-state and mutable data

Pure functions
- It returns the same result if given the same arguments
- ` let PI = 3.14; ` ` const calculateArea = (radius) => radius * radius * PI; ` ` calculateArea(10); // returns 314.0 `
- It does not cause any observable side effects
let counter = 1;function increaseCounter(value) {counter = value + 1;}increaseCounter(counter);console.log(counter); // 2
_ pure functions:
- It returns the same result if given the same arguments.
-
It does not cause any observable side effects.
- EX: impure function:
- let PI = 3.14;
- const calculateArea = (radius) => radius * radius * PI;
- calculateArea(10); // returns 314.0
- Immutability:
- Unchanging over time or unable to be changed.
- When data is immutable, its state cannot change after it’s created.
- If you want to change an immutable object, you can’t.
- Instead, you create a new object with the new value.
Referential transparency
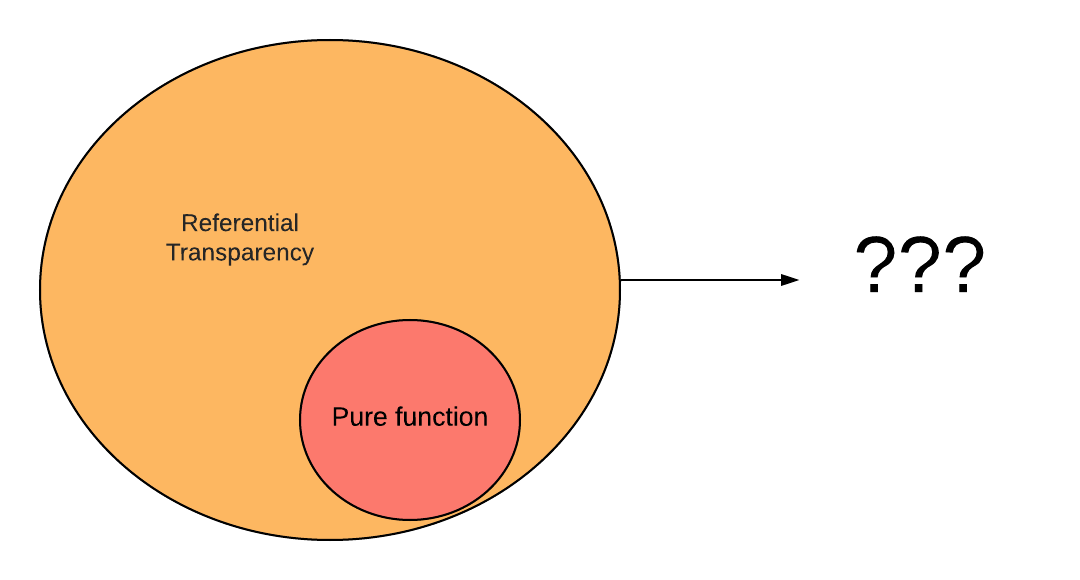
- Basically, if a function consistently yields the same result for the same input, it is referentially transparent.
- ` pure functions + immutable data = referential transparency `
Standards
- There is no doubt that standards help to improve the quality of code. It’s important to check for those standards while refactoring your code